BarCodes Types:
| Code 39 | 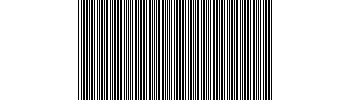 |
| Code 93 | 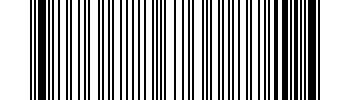 |
| Code 128 |  |
| EAN |  |
| 2 of 5 |  |
| datamatrix | 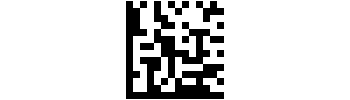 |
| aztec |  |
| codabar |  |
| pdf417 |  |
Barcodes are machine-readable representations of data, typically displayed as patterns of bars and spaces, used for identification and tracking across industries like retail, logistics, and manufacturing. They enable quick data retrieval by being scanned with optical devices, which decode the patterns into usable information.
Barcodes come in various formats, each with unique structures and applications:
UPC (Universal Product Code): A 12-digit numeric barcode prevalent in North American retail for product identification at point of sale.
EAN (European Article Number): An international standard similar to UPC, available in EAN-13 (13 digits) and EAN-8 (8 digits) versions for global use.
Code 39: An alphanumeric barcode that encodes letters, numbers, and select symbols, widely used in inventory management and industrial applications.
Code 128: A high-density barcode capable of encoding all 128 ASCII characters, suited for shipping and packaging due to its compact data storage.
| Code 39 |  |
| Code 93 |  |
| Code 128 |  |
| EAN |  |
| 2 of 5 |  |
| datamatrix |  |
| aztec |  |
| codabar |  |
| pdf417 |  |